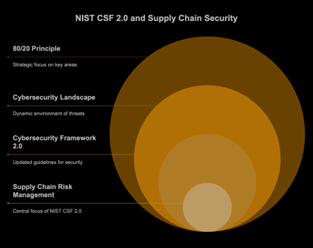
Navigate NIST CSF 2.0’s supply chain security updates with the 80/20 principle. Prioritize risks and resources for maximum impact in the evolving threat landscape.

The cybersecurity landscape is in constant flux, with new threats emerging daily, particularly within the intricate web of supply chains. Recognizing this, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has released its updated Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0, bringing significant enhancements, especially in addressing supply chain risk management (SCRM).
This blog post explores these crucial changes and demonstrates how the 80/20 principle can be a powerful lens for implementing them effectively by focusing on the 20% that truly matters.
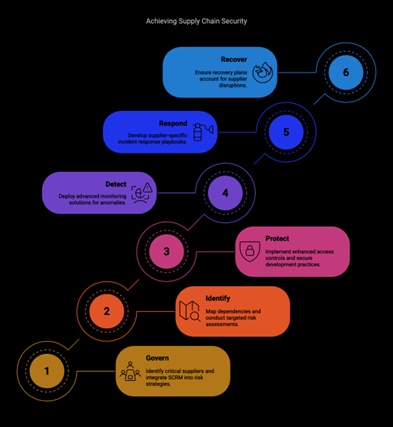
NIST CSF 2.0 introduces a stronger focus on supply chain security through its new GOVERN (GV) Function and Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management (C-SCRM) category. By applying the 80/20 principle, enterprises can prioritize their efforts on critical suppliers, vulnerabilities, and components that pose the most significant risks. This blog outlines actionable strategies for CISOs and CIOs to align their supply chain security posture with NIST CSF 2.0 while optimizing resource allocation for maximum impact.
The modern enterprise is deeply interconnected, relying on a complex network of suppliers, vendors, and third-party partners to operate efficiently. However, this interconnectedness also introduces vulnerabilities. Supply chain attacks like SolarWinds and Log4j have demonstrated how adversaries exploit these relationships to infiltrate organizations at scale.
In response to this growing threat, NIST CSF 2.0 emphasizes supply chain risk management as a core component of cybersecurity strategy. For CISOs and CIOs, this update provides both a challenge and an opportunity: how to manage these risks effectively without overwhelming resources. Enter the 80/20 principle, which offers a pragmatic approach to focus on what matters most.
Supply chain attacks are on the rise, with reports indicating that 62% of organizations experienced a supply chain-related cyber incident in 2023 (source: Gartner). These attacks are not only increasing in frequency but also in sophistication, targeting trusted suppliers to bypass traditional defenses.
Key challenges include:
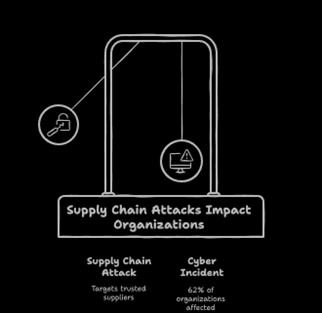
These challenges underscore the need for a structured approach that prioritizes high-impact risks while aligning with evolving frameworks like NIST CSF 2.0.
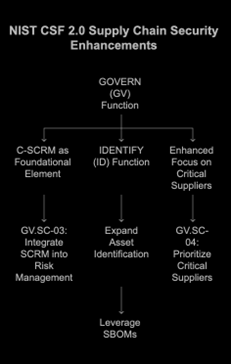
The updated framework introduces significant enhancements to address supply chain risks:
The Pareto principle suggests that 80% of outcomes stem from 20% of causes—a concept that resonates deeply in cybersecurity resource allocation:
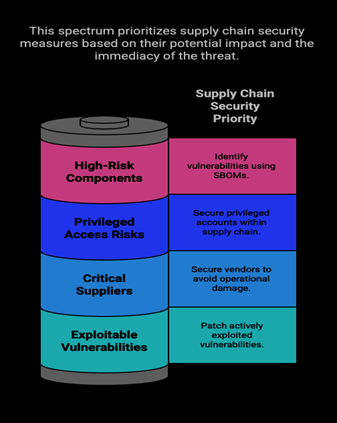
By targeting this “critical 20%,” enterprises can achieve outsized security gains without overextending resources.
Leading organizations are already applying these principles effectively:
As supply chains grow more complex, regulatory scrutiny will continue to rise, pushing enterprises toward greater accountability for third-party risks. Emerging technologies like AI-driven threat intelligence will further enhance visibility into supplier ecosystems but will require careful integration into existing frameworks like NIST CSF 2.0.
Key takeaways for CISOs/CIOs:
NIST CSF 2.0 provides a robust framework for strengthening your supply chain security posture while aligning with evolving regulatory demands. By strategically applying the Pareto principle, CISOs and CIOs can focus their limited resources on the most critical risks, achieving greater resilience without unnecessary complexity.
Ready to take your supply chain security strategy to the next level? Contact us today for a consultation or download our whitepaper on implementing NIST CSF 2.0 effectively!
Post Tags :
Share :

Assess. Measure. Fortify.
Keep Your Assets Safe With Our
Cutting-Edge Cybersecurity Solutions.
Developed by HACKTRONIAN